implementation of the main memory management in paceval
More...
implementation of the main memory management in paceval
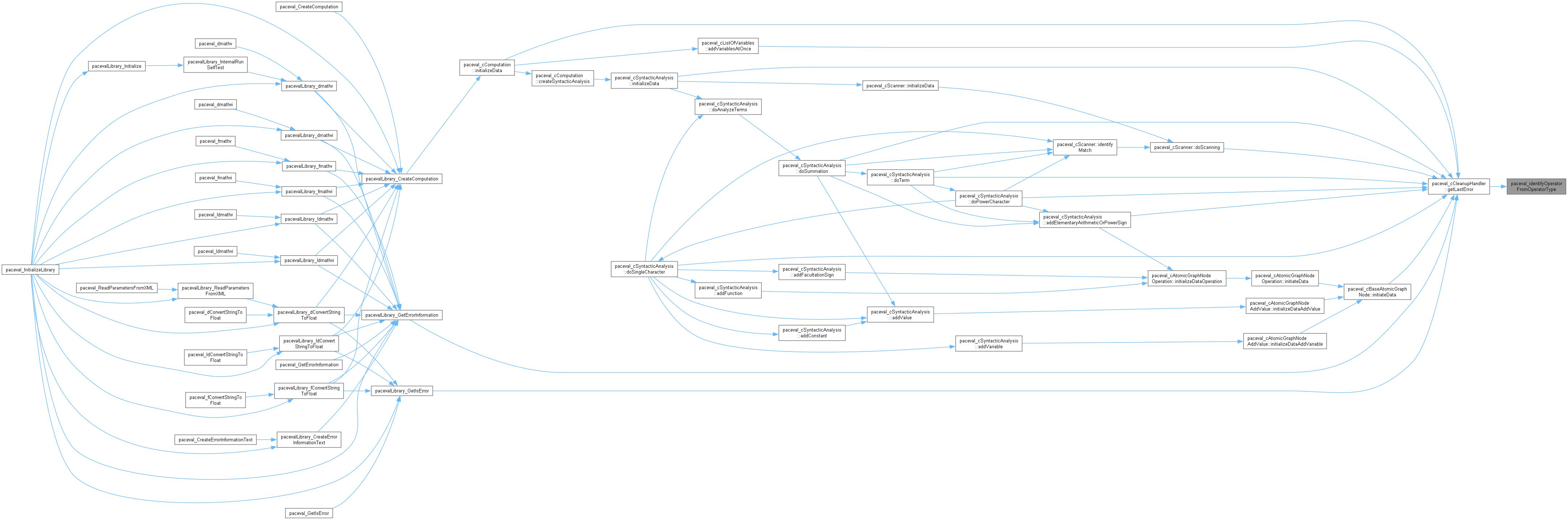
implementation of the data types, objects and classes required in paceval that are responsible for memory management (e.g. paceval_cRegisteredObject and paceval_cCleanupHandler) and error handling (e.g. paceval_sErrorInformation)
◆ paceval_max_logging_buffer
| #define paceval_max_logging_buffer 25000 |
◆ paceval_deleteLoggingMemory()
| bool paceval_deleteLoggingMemory |
( |
| ) |
|
deletes the memory buffer used for logging, which empties it
◆ paceval_getCurrentTime()
| unsigned long paceval_getCurrentTime |
( |
| ) |
|
gets the current time in milliseconds since the system started
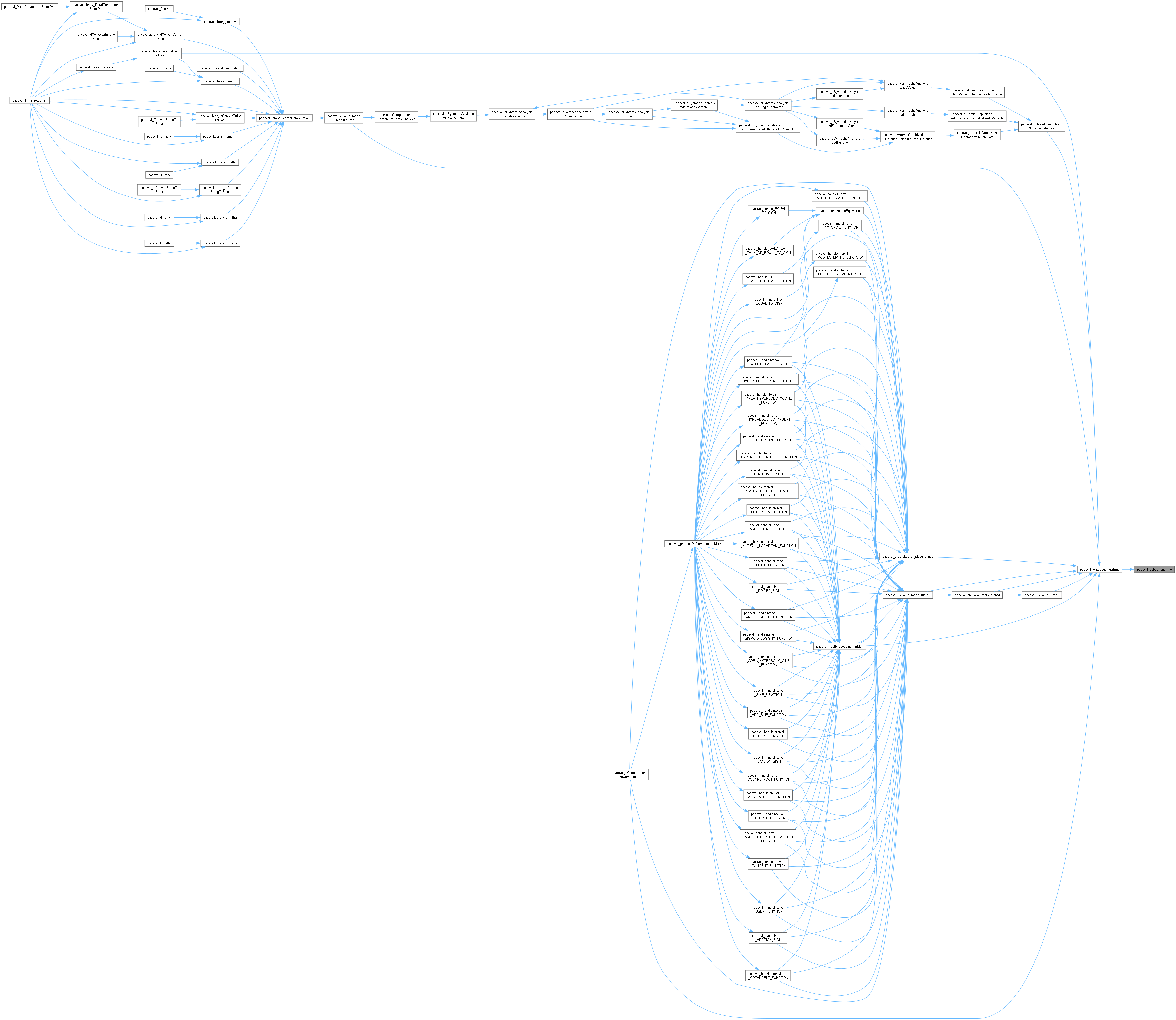
◆ paceval_identifyOperatorFromMathematicalCharacter()
forward declaration - gets the current time in milliseconds since the system started (see paceval_cCleanupHandler.h) identifies the associated type of paceval_eOperatorTypes for a type of paceval_eMathematicalCharacterTypes, e.g. the associated ADDITION_SIGN for ADDITION_CHARACTER (see paceval_cCleanupHandler.cpp)
- Parameters
-
| eMathematicalCharacterType_in | specifies the type of paceval_eMathematicalCharacterTypes |
◆ paceval_identifyOperatorFromOperatorType()
| void paceval_identifyOperatorFromOperatorType |
( |
char * | operator_out, |
|
|
paceval_eOperatorTypes | eReturnOperator_in ) |
identifies the operator (e.g. "+") from the type of operator (e.g. ADDITION_SIGN)
- Parameters
-
| operator_out | specifies the buffer for the operator |
| eReturnOperator_in | specifies the type of operator to look for |
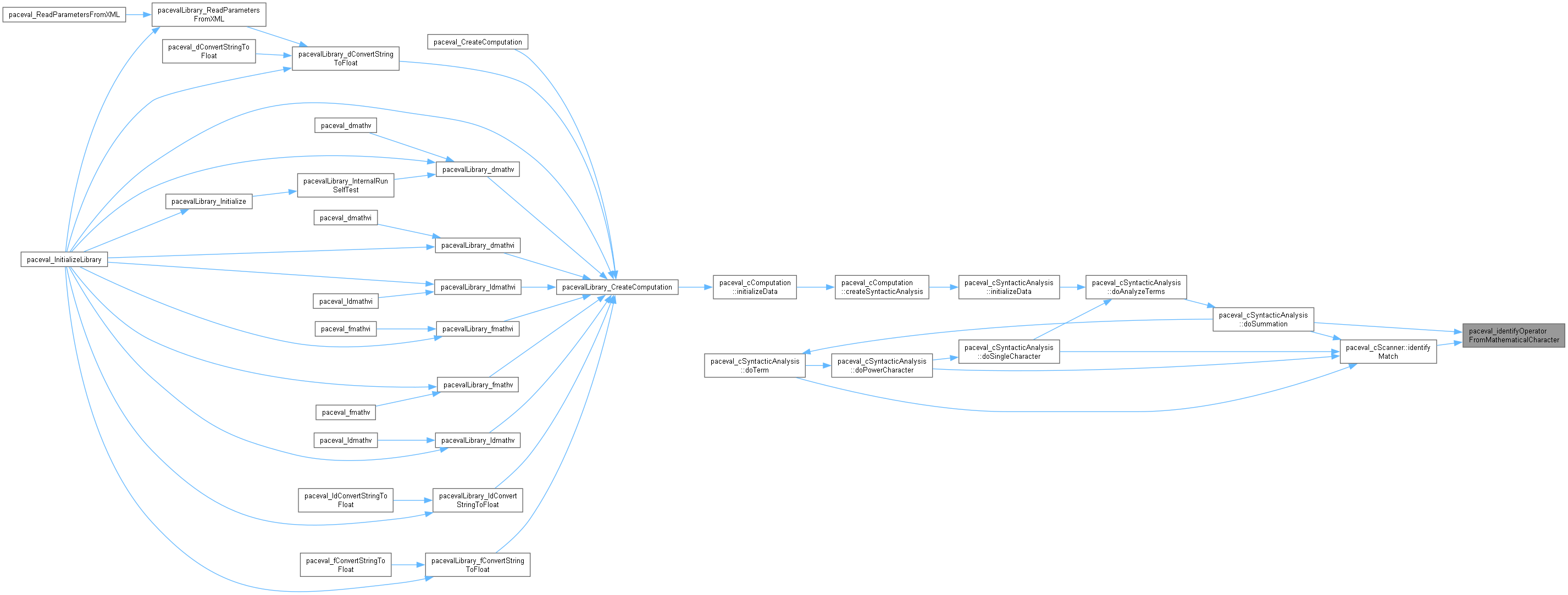
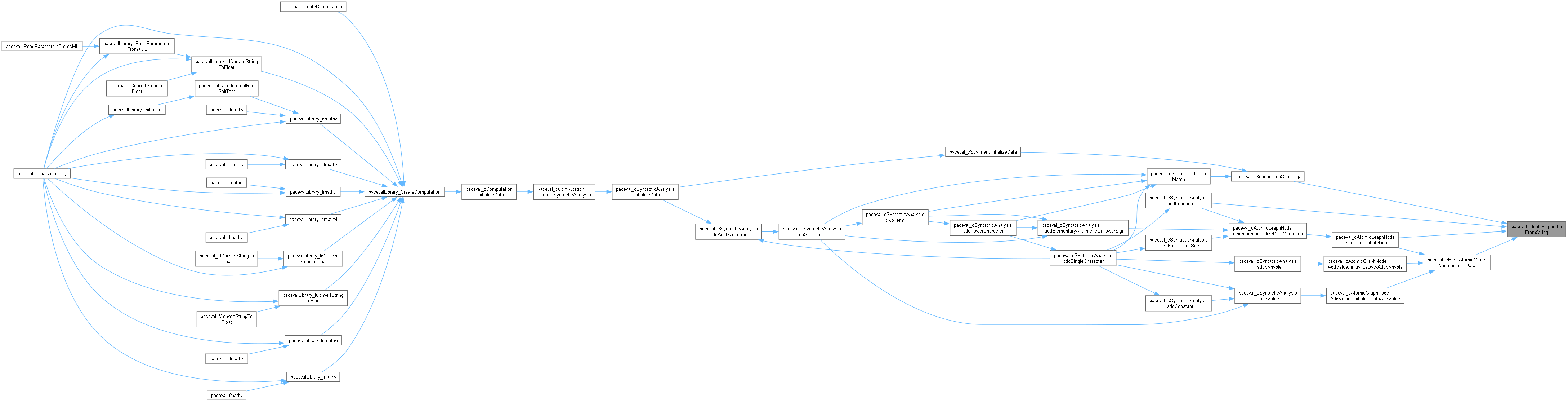
◆ paceval_identifyOperatorFromString()
| paceval_eOperatorTypes paceval_identifyOperatorFromString |
( |
const char * | operator_in, |
|
|
long | valueNode2_in, |
|
|
const char * | valueOperator_in ) |
identifies the type of operator (e.g. ADDITION_SIGN) based on the associated parameters
- Parameters
-
| operator_in | is the character string that contains the operator (e.g. ":=", "+" or "sin") |
| valueNode2_in | specifies the node of the possible second operand (e.g. the operator "y" for "x+y") |
| valueOperator_in | specifies the numerical value to convert when ":=<floating point number>" (SET_TO_VALUE_SIGN) |
◆ paceval_lockGlobalVariables()
| bool paceval_lockGlobalVariables |
( |
| ) |
|
◆ paceval_setCallbackUserFunctionString()
| void paceval_setCallbackUserFunctionString |
( |
unsigned int | numberUserFunction_in, |
|
|
const char * | singleFunctionString_in ) |
allows the definition of up to 1000 custom user functions (see pacevalLibrary_SetCallbackUserFunction())
- Parameters
-
| numberUserFunction_in | specifies the number of the user function to set the single function for (e.g. 1) |
| singleFunctionString_in | specifies the user-defined single function (e.g. "my_function1") |
◆ paceval_unlockGlobalVariables()
| void paceval_unlockGlobalVariables |
( |
| ) |
|
◆ paceval_writeLoggingString()
| void paceval_writeLoggingString |
( |
const char * | loggingString_in | ) |
|
writes data for logging with a time stamp into a memory buffer and, if paceval_ENABLE_LOGGING_TO_FILE is set, into the file "paceval_loggingFile.log"
- Parameters
-
| loggingString_in | specifies the string to add to logging |
◆ pacevalLibrary_GetLoggingInformation()
| int pacevalLibrary_GetLoggingInformation |
( |
char * | paceval_loggingInformation_out | ) |
|
returns the string of the logging information - the return value is the length of the logging string
- Parameters
-
| paceval_loggingInformation_out | points to the buffer that will receive the string (set paceval_strVersion_in to NULL to receive the length of the logging string) |
◆ paceval_callbackUserFunctionString
◆ paceval_loggingMemory
| char* paceval_loggingMemory = NULL |